Budgeting your medical billing costs correctly is a core requirement for any healthcare practice. Setting the right budget ensures you cover operational costs and maintain healthy cash flow for your clinic. However, hidden fees and confusing pricing models of medical billing companies make correct budgeting hard.
A lack of clarity in your billing approach can cause initial claim denials, which averaged about 11.8% in 2024, according to Kodiak Solutions. Those denials aren’t cheap. An estimate shows that healthcare providers spend up to $20 billion annually on reworking these denials. Worse, as many as 50% to 65% of denied claims never turn into revenue.
All these denials directly reduce the return on investments while increasing the revenue leakages. Hence, choosing the right medical billing partner to handle billing costs is essential for a practice. This guide explains billing cost structures and proven pricing strategies to help your practice protect revenue.

Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Understanding Medical Billing Costs Matters for Your Practice
Rising denials, stretched cash cycles, and hidden fees cause bookkeeping headaches and cut directly into cash flow and work efficiency. Here’s why every provider should track medical billing costs closely:
1. Billing Costs Directly Affect Profit Margins
Every dollar spent on billing reduces possible revenue, whether for staff, software, clearinghouse fees, or outsourcing. Many practices underestimate how much of their collections go back into billing. Hence, knowing the true cost of medical billing and coding helps measure profit more accurately.
2. Cost Clarity Enables Smarter Business Decisions
An accurate idea of your medical billing costs helps your practice make better financial and operational decisions. With clear numbers, you can compare in-house billing to outsourcing and check if your current system is efficient. Without this clarity, many practices rely on guesswork, which often leads to overspending.
3. Untracked Costs Hide Inefficiencies
Billing is more than submitting claims. It also includes follow-ups, appeals, patient collections, compliance, and technology upkeep. If you do not track these expenses, inefficiencies build up quietly and reduce revenue without being noticed.
4. Better Cost Awareness Supports Scalability
As your practice grows, your billing needs will also grow. So, understanding costs now helps you plan for the future medical billing service costs. This may mean adding staff, upgrading software, or renegotiating contracts with a billing company.

5. Cost Visibility Improves Cash Flow Management
You might think billing is only an expense. Instead, it is directly connected to collections. If billing costs go up but reimbursement or cash flow does not improve, the practice loses money. Watching costs and collections together keeps the revenue cycle healthy.
Key Factors Influencing Medical Billing Cost
Billing costs vary by practice size, specialty, and payer environment. These five drivers determine how much you’ll spend and how much revenue you’ll actually keep:
1. Billing Method: In-House vs. Outsourced
The most important factor is what approach you take to handle the medical billing. An in-house team includes expenses like salaries, benefits, training, software, and ongoing compliance. On the other hand, the cost of outsourcing medical billing can include a percentage of collections or a flat per-claim fee.
2. Practice Size and Volume
Whatever billing approach you choose, the complexity of your practice’s operation and the claim volume directly affect the cost. Larger practices with higher patient volume can benefit more from paying a percentage of collections. In contrast, small clinics with lower volume may prefer a per-claim rate.
3. Specialty and Complexity of Services
Specialties like cardiology, oncology, and orthopedics have harder coding rules. CMS audits often find problems with medical necessity and coding errors. To correct these requires paying higher rates, leading to higher costs of medical billing and coding.
4. Payer Mix and Contract Requirements
Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial payers each have their own denial trends, payment schedules, and authorization rules. Practices that rely on a mix of these payers often face higher admin costs and slower payments, especially when prior authorizations are common.
5. Denial Volume and Resubmission Workload
The share of denied claims that go unworked has a direct impact on collections. Studies show that only one-third of denied claims get resubmitted. That means two-thirds of possible revenue is lost if no one follows up, increasing your medical billing costs.
Pricing Models for Medical Billing Services
Medical billing service providers structure their fees in different ways. Understanding each model’s mechanics, benefits, and risks helps you compare options effectively.
1. Percentage of Net Collections
This is the most widely used approach. Medical billing companies take a share, typically 4% to 10% of net collections, with 5% to 8% most common. The fee scales with revenue, aligning incentives to collect more, making it the preferred choice for many.
If denials stay high or days in A/R remain long, a practice can lose much more than the quoted percentage. Transparency on collections, adjustments, and what is being offered is essential for judging value. Trusted billing companies such as Transcure provide this level of clarity.
2. Per-Claim Model
In this model, medical billing services charge a fixed amount per processed claim, often $4 to $10 per claim. It works well for smaller practices with low claim volume or those performing high-value procedures. The benefit of this medical billing cost model is predictable finance control.
As for the drawback, the medical billing company earns the same regardless of whether claims are paid quickly. This means practices shoulder the risk of denials, rework, and long A/R cycles without any accountability for the outsourced service provider.
3. Hourly or Staff Augmentation
Some practices outsource billing staff by the hour or use third-party firms to provide coders and claim processors. Rates vary by skill and geography, but costs are generally higher if the efficiency of the work is low. This model offers staffing flexibility and oversight for the primary work.
However, it shifts responsibility for denial prevention and collections back onto the practice. Without strong internal workflows, it can become labor-heavy and more expensive than performance-based pricing.
4. Hybrid Models
Hybrid pricing blends approaches, for example, a percentage fee for collections plus a flat rate for prior-authorization or patient statements. This structure can provide balance by aligning incentives while keeping certain costs predictable.
The downside is complexity: practices must review contracts carefully to avoid hidden charges. If the setup is poor, hybrids can cut into margins, especially if the chosen billing company doesn’t improve denial rates or A/R days.
Cost of Medical Billing Services: In-House vs Outsourced Billing
With a better idea of how much does it costs to outsource medical billing under different models, you might wonder about managing billing on your own. Be it in-house billing or outsourced to a service provider, both approaches have very different cost structures:
In-house billing model
Doing billing in-house means hiring staff, paying for software, and covering training and oversight. Billing specialists earn about $50,250 a year, says the Bureau of Labor Statistics. With benefits and overhead, that cost is closer to $65,000 per full-time employee.
Practices also pay for clearinghouse fees, IT support, and compliance updates. The benefit is full control, but the drawback is high fixed costs and reliance on staff.
Outsourced Billing Model
When you opt for a medical billing company, most usually charge 3% to 10% of net collections, with 5% to 8% most common. This directly links your medical billing and coding costs to your revenue. Strong service providers handle denials, appeals, and reporting in the package.
This often improves A/R days and lowers denials for your practice. The downside is less control and the need to check contracts closely to avoid extra fees for statements, tech, or prior authorizations.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Dimension | In-House Billing | Outsourced Billing |
|---|---|---|
| Direct cash cost | Fixed: salaries + benefits for billing FTEs, management, software, and clearinghouse fees. | Variable: medical billing service fee, usually 4 to 10% of net collections or $4 to $10 per claim. |
| Denial handling | Full control, but denials consume internal time; appeals depend on staff expertise. | Appeals are often included in the vendor fee; strong billing service providers lower denial rates. |
| Cash flow / Days in A/R | May lag if staff are stretched; payroll is a fixed expense regardless of collections. | Often improves A/R since billing companies specialize in follow-up, but the impact depends on service quality. |
| Scalability | Requires new hires and training as volume grows, creating step-cost jumps. | Scales smoothly with revenue; good for fast-growing or multi-site practices. |
| Control & visibility | Maximum operational control and direct oversight of staff and processes. | Dependent on vendor transparency, require dashboards and data export rights. |
| Technology & automation | Practice pays for EHR, billing systems, licenses, and upgrades. | The chosen medical billing firm typically provides clearinghouse access, automation tools, and reporting. |
| Best fit | Larger, stable practices with strong in-house RCM expertise. | Practices want a predictable cost-to-revenue ratio or those lacking billing staff depth. |
Worked Example: In-House vs Outsourced Billing
Assumptions (Hypothetical Practice Financials):
- Net Collections: $1,000,000 per year
- Claims: 10,000 per year
- Initial Denial Rate: 12%
- Rework Cost Per Denial: $50
- Staff Salaries: $50,250/year (BLS median), loaded cost ≈ $65,325/FTE
- Staff Required: 2 FTEs
- Software: $6,000/year
- Clearinghouse: $6,000/year
- Management and Overhead: $20,000/year
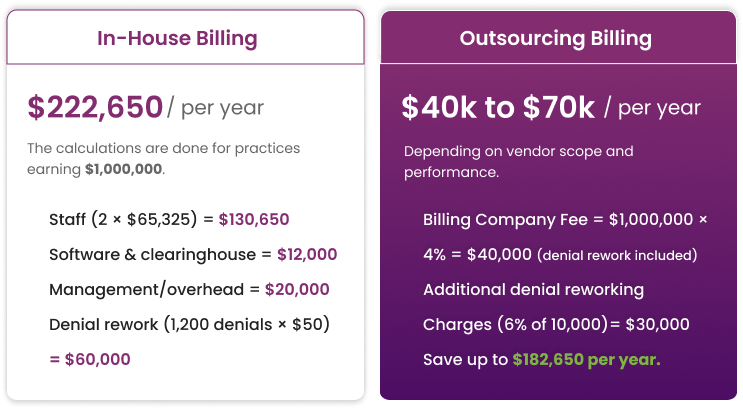
Scenario A: In-House Billing
- Staff (2 × $65,325) = $130,650 per year
- Software and Clearinghouse = $12,000 per year
- Management and Overhead = $20,000 per year
- Denial Rework (1,200 denials × $50) = $60,000 per year
- Total = $222,650/annum
Scenario B: Outsourced Billing
- Medical Billing Company Fee = $1,000,000 × 4% = $40,000/ annum
- Denial Rework: usually included in the chosen plan, especially for those charging a revenue percentage.
- When not, the vendor impact reduces denials (12% to 6%), so the potential residual = $30,000
- Total = $40k to $70k per year, depending on what chosen billing service offers and its performance.
By opting to outsource your billing to a medical billing company, you can save up to $182,650 to $152,650 per year.

What Outsourcing Billing Really Means for Your Practice’s Expenses
Outsourcing medical billing is one of the fastest ways for practices to cut overhead and stabilize revenue. Instead of paying fixed salaries, benefits, and software costs, you pay a predictable percentage of collections. This model directly ties billing cost to performance, while also reducing denial rework and shortening days in A/R.
This is where Transcure comes in. Unlike generic medical billing providers, Transcure operates as a full-cycle RCM partner. With teams across 40+ specialties, we work for surgical centers, pain management, dental, and many others. Our advanced automation tools help practices minimize errors and reduce claim denials.
As a result, your reimbursements accelerate by up to 15%. Moreover, Transcure charges just 4 to 5% of total practice revenue, based on actual collections from insurers. This makes billing transparent and directly tied to your practice’s success.
What Transcure Delivers for Your Practice
- Clean-claim Scrubbing and Automation: Up to 98% of your claims get approved at the first submission, which keeps the costly rework and hidden denial expenses to a minimum.
- Denial Management and Free Resubmissions/Appeals: Every denied claim is followed up by Transcure until it has been fixed, so you don’t lose revenue.
- Credentialing and Payer Enrollment at No Extra Cost: The addition of complementary credentialing speeds up approvals and avoids payment delays tied to enrollment.
- Patient Billing Statements and Eligibility Checks Included: Transcure helps collect money upfront and lowers unpaid balances without extra fees.
- Active A/R Management: By keeping days in A/R to less than 40, Transcure improves cash flow stability for your practice.

Strategies to Keep Medical Billing and Coding Costs Down
Most practices already know they should “reduce denials” or “train coders” to lower their medical billing costs. The real savings come from managing billing costs at a structural and contractual level. Here are strategies that go beyond the obvious:
1. Look Past the Fee Percentage
When outsourcing the cost of medical billing and coding, you might have two medical billing companies that both charge 5% of collections. So, look at proposal details as some include denial resubmissions, credentialing, and patient statements for free.
Others charge extra for them. Comparing services side by side can save practices up to 15% in hidden costs without changing the fee rate.
2. Consolidate RCM and Credentialing
Many practices pay separately for credentialing or payer enrollment consultants as part of their cost of outsourcing medical billing. Choosing a billing partner like Transcure that bundles credentialing avoids double fees and speeds up payment by stopping claim holds tied to enrollment.
3. Automate Eligibility and Patient Verifications
Errors at the start of the cycle cause bigger billing costs later. If you check insurance and estimate what patients owe before billing, you cut write-offs and need collection agencies less. This step can lower patient collection costs by 20% to 30%.
4. Monitor A/R Efficiency
A practice might have normal denial rates but still lose money if follow-up on A/R is poor. Check how many days your medical billing company keeps claims in A/R. As the benchmark is 30 to 40 days, add rewards or penalties based on those numbers. This pushes them to work faster and lowers costs from slow cash cycles.
Hidden Costs to Watch Out For
Medical billing service costs often look straightforward on paper, but practices frequently discover extra charges that weren’t in the initial proposal. Here are the most common hidden costs to monitor:
1. Denial Rework Not Included
Some medical billing services do not include claim resubmissions or appeals in their base fee. With rework costing up to $117 per denial, this can quickly exceed the savings you got from a lower base percentage.
2. Patient Billing Statements and Support
Mailed statements, payment portals, and call-center support are sometimes billed separately. You might end up paying per statement or per patient call, adding thousands annually.
3. Setup and Termination Fees
When you choose a new medical billing company, some demand “startup” fees for data migration or EHR integration. Likewise, the old ones can add termination penalties or block data transfer, making switching costly.
4. Software and Clearinghouse Charges
Apart from the direct cost of outsourcing medical billing, practices can still be billed for clearinghouse access, claim scrubbing, or patient portals if these aren’t included. Over time, this can add up to rival the cost of an extra FTE.
5. Lost Revenue from Slow A/R Follow-Up
Not all costs you will face will be in the form of direct fees. If your selected medical billing service does not actively chase outstanding claims, collections will go down. It will lead to rising write-offs, putting significant strain on your cash flow.

Conclusion
Medical billing costs directly shape your practice’s financial health. From denial rates to company contracts, every decision affects cash flow, staff workload, and patient satisfaction. The choice is not about price itself. It’s about predictable costs, fewer revenue leaks, and measurable ROI.
That’s why many practices move to outsourcing with a partner like Transcure. By charging only 4% to 5% of collections, it includes services from credentialing to patient billing at no extra cost. It allows Transcure to help practices lower expenses while improving collections.
FAQs on Medical Billing Cost
What is the cost share in medical billing?
Cost share is the portion of healthcare expenses patients pay directly, including copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. It does not cover the provider’s billing costs but directly impacts patient collections and overall practice revenue.
What is the average medical billing service cost for small clinics?
Small clinics typically pay 5% to 8% of net collections for outsourced billing services. Some charge per claim ($4 to $10 each), but percentage-of-collections remains the most common and scalable pricing model for smaller practices.
How do medical billing costs differ by specialty?
Specialties with complex coding (e.g., cardiology, oncology) face higher denial risks and often pay slightly higher billing fees. Simpler and high-volume specialties like family practice and internal medicine usually secure lower rates, as claims are easier to process and recover.









